External Influences on Business Activity (6.1)
- Thiago Casarin Lucenti
- Aug 18, 2025
- 10 min read
Chapter 6 - External Influences on Business Activity
Learning Objective: 6.1 External Influences on Business Activity
It's no news that the only constant is change. Businesses operate in dynamic environments compromised of laws, political and social factors, economic conditions, level of technology, competitors and suppliers, international trade links, and environmental pressures.
Decision-making is closely dependent on such external forces which, therefore, need to be thoroughly understood.
6.1 Political and Legal Influences:
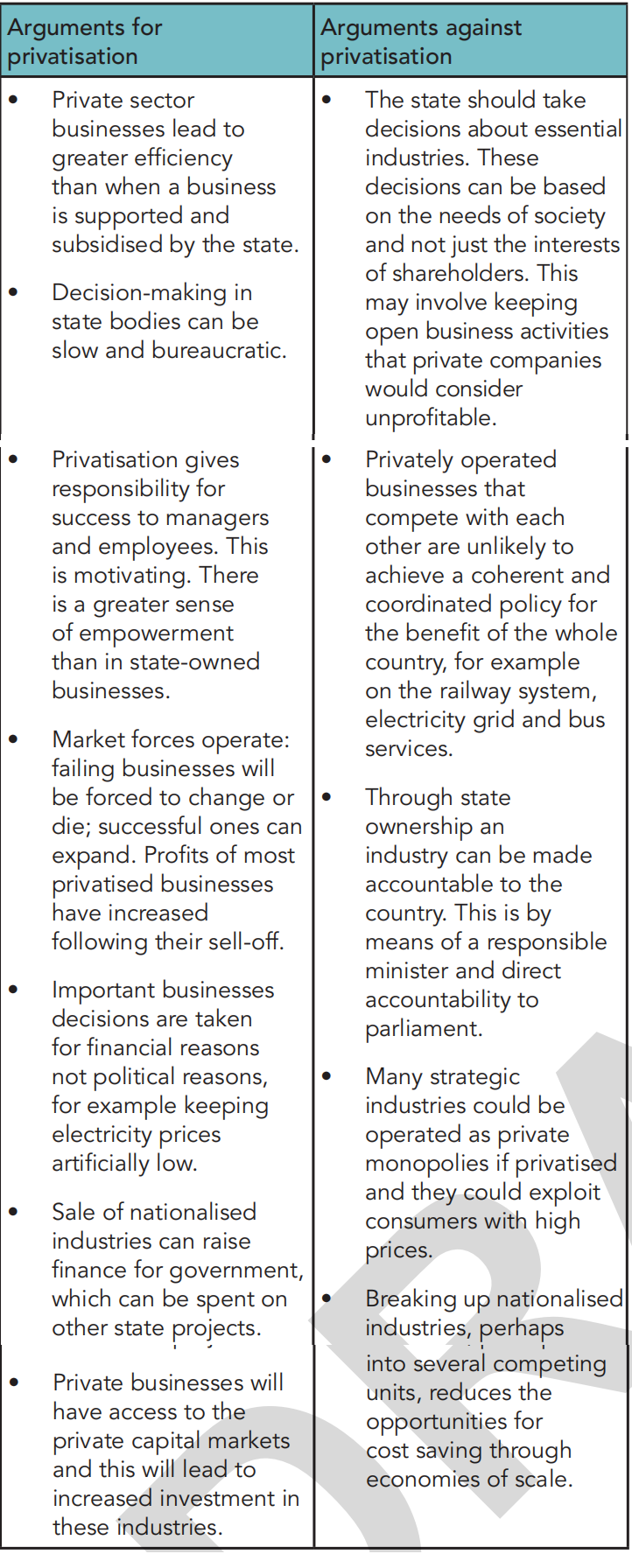
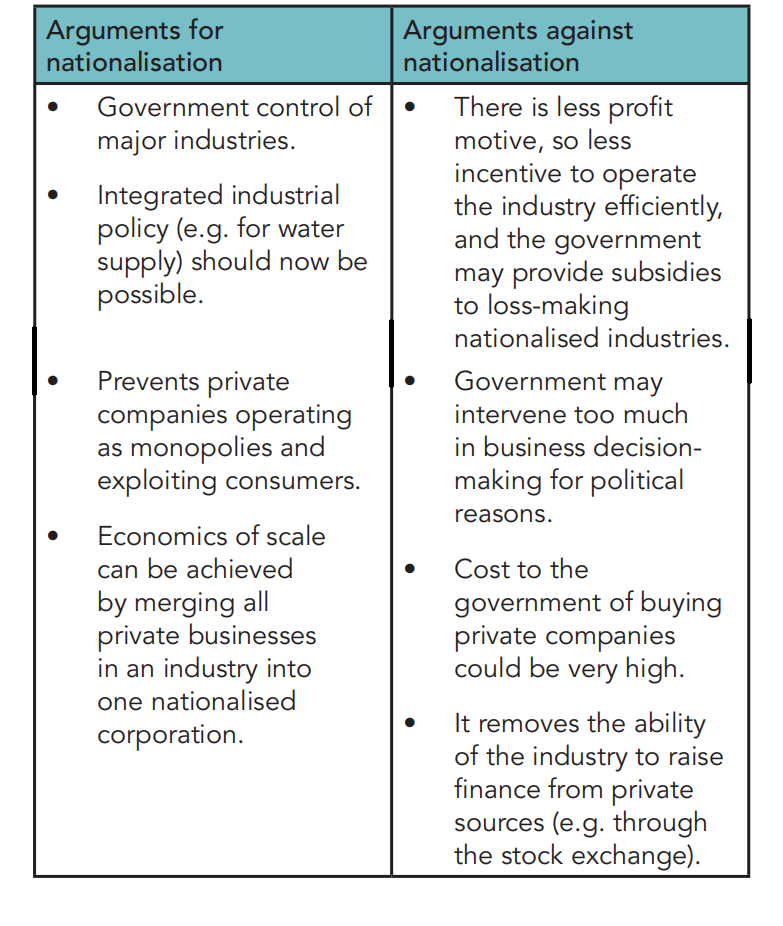
Are you for privatization? Against it? For nationalization? Against it?
Privatization: selling state owned businesses to private investors (e.g. British Airways).
Nationalization: transfer of private owned businesses to state ownership/control (e.g. AIG).
Prepare a Debate (Research) on the Nationalization of Oyu Tolgoi (OT) by the GoM:
We should also know that legal constraints impact business activity in different ways:
Employment Practices to prevent the exploitation of workers by employers:

Recruitment practices;
Minimum wages;
Health and safety at work (training, protective equipment, breaks, facilities);
Contracts and termination.
Examples:
Maximum weekly working hours can be long – 52 hours in Central African Republic, but only 37 hours in Denmark;
No minimum wage law in Sweden, Norway and Denmark;
Minimum working ages vary; for example, just 10 years old in Sri Lanka.
These differences (among many others) are driving the location decisions for some multinational companies as tighter regulations usually mean higher business costs. On the other hand, having high standards can increase employee morale and motivation, attract qualified workers, helps avoiding accidents, and creates good publicity for businesses.
Another field in which governments create legal controls is regarding marketing behavior and consumer rights. Such laws are there to protect customers against business activity:

Large marketing and advertisement budgets are influential and can mislead consumers;
Sales techniques that might lead customers into high debt are on the spotlight;
Quality and safety standards are developing to avoid poor-quality imported items (globalization);
Minimum guarantee periods and service are sometimes mandatory.
Complying with such laws, once again, increase some business costs due to the need of redesigning products to meet health and safety laws and redesigning ads to be less persuasive and less precise, for example.
On the other hand...
Bad publicity can be avoided as well as court actions (fines) due to faulty products;
Increased customer loyalty;
Good reputation for quality and honest advertising.
Although some of these regulations may seem and sound fair. How about government control over competition?

Many countries out there investigate and control monopolies — companies that own 25% or more of the market - by not approving mergers and takeovers (M&A). This is all for the sake of protecting customers from lower quality, high priced, limited options of products and services. The justifications for such interventions are various:
‘Monopolized industries tend to be less innovative (lower investment on R&D from monopoly businesses).’
‘Monopolies act against customers’ interest by charging higher prices and offering lower quality.’
‘Monopolies lead to limited customer options.’

Collusion is another business practice oftentimes limited by regulations:
- Businesses are not allowed to agreeing and fixing prices so that competition is restricted in the marketplace.
Activity 6.4 (p. 79)
Social and demographic changes can also influence business' decisions such as, for example, which products to supply to the market. Let's discuss an important force that has been gaining momentum for some time now:
The increasing importance of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):
Businesses that follow their legal and moral obligations with all of its stakeholders (not only investors) are said to be showing CSR. Such businesses usually show a greater concern for their decisions regarding the environment and the society around them.
Here are a few things businesses should pay attention to in order to be considered socially responsible:

- Accounting Practices (inflation of value to attract lenders/investors);
- Payment of Illegal Incentives (i.e. bribes to get ahead or avoid punishments);
- Social Auditing: a report on the impact a business has on society (issued annually).
- Growing popularity/importance;
- Not a legal requirement yet.
Social Audits Include:

- Health and safety record (e.g. # of accidents);
- Pollution levels;
- Contributions to society and charities;
- Fairtrade suppliers;
- Employees' benefit scheme;
- Measures for annual target of social responsibility;
- Feedback from customers/suppliers.
Businesses that consider the community needs improve their image to customers and investors, increase the chance of being accepted by the community (expansion/relocation), are more likely to receive grants, reduce action of pressure groups:

Pressure Groups act upon three main areas:
- Pushing businesses to change policies and cause less environmental damage;
- Convincing customers to support socially responsible businesses and boycott the others;
- Lobbying governments to create laws and regulations that support their agenda.
How do pressure groups achieve their objectives?
- Pressure Groups make public the activity of businesses that do not follow their agenda and try to influence the public opinion through demonstrations, boycotts, and campaigns.
- Changing consumer behavior and make a business lose sales is also an effective tool for such groups.
- Lobbying the government to change their policies regarding different issues (ethical, environmental, etc.) by, sometimes, damaging its popularity.
Another category of external changes that heavily influence business activities is Demographics Changes. There are many phenomena to exemplify such changes:
Think of Japan's aging population problem:
The number of active workers has been rapidly decreasing as the amount of government-dependent retirees keeps rising. Active workers have been facing increased tax burdens so that the government can afford for the welfare of the elderly population.
At the same time, the demand patterns of an aging population turns out to be very different - businesses have been deeply affected by such changes.
Aging, however, is just one of the social/demographic factors that can heavily influence business activities:
The changing role of women in today’s society, for example, has caused many impacts to businesses:
As women keep on taking higher paying jobs the demand for goods and services that interest this specific female population increases;
Moreover, more women inserted in the workforce has also led to smaller families and even to an increase in divorce rates - both of which greatly impact overall consumption (e.g. a single household has very different demands than a large family does).
Interesting fact:
Did you know that over 70% of the Mongolian population at the age to join college and university do so?
This great increase in higher education holders has been causing positive and negative implications to businesses. For example:

A higher educated population leads to an increase in skilled and flexible workforce, which highly benefits businesses;
However, a skilled and flexible workforce demand higher salaries bringing business costs up;
Moreover, the increase in the average income of an educated population can be positive to business as the disposable income of this population can cause an increase in demand for products and services.
Also, the changes in patterns of employment is an important one taking place in many countries worldwide:

Labor is being replaced by technology in many places;
Labor has switched from old-established industries (e.g. steel) to high-tech ones;
Increased number of women in various occupations;
Increase in part-time employment;
Raise in flexible working patterns (e.g. working from home);
Increase in the dependency ratio due to aging population.
Changing social conditions and employment patterns can create just as many opportunities for businesses as potential risks or threats.
As you can see, many social and demographic changes that at first glance seem irrelevant to business can actually lead to great impacts. A much more obvious external influence on business activity relates to technological developments:
The quick development of Information Technology (IT) has been aiding businesses decision-making for different reasons:
A much greater amount of information and data can be quickly collected and analyzed with the help of technology leading to better and faster decisions;
Information systems have also been revolutionizing communications: transmitting information has never been quicker and more efficient than today.
However, IT can also be seen as a troubling factor for decision-making in some instances:

The amount of information that workers and managers are exposed to currently is immense causing great stress by information overload;
Furthermore, managers started being given less authority to make decisions since IT systems are better at collecting and analyzing information - causing a decrease in job enrichment and a consequent fall in motivation and productivity.
New technology is not the best solution to all problems and introducing it badly can create more problems than it solves. For introducing technology effectively businesses should:
Thoroughly analyze how the technology can improve the business effectiveness;
Involve all managers and workers related to the new technology as better ideas are more likely to raise from the workers who will use it than the managers who will buy it;
Evaluate the different systems available (cost, efficiency, productivity gains) considering the available budget;
Monitor the introduction and use of the new technology: is it as efficient as previously thought? If not, how can it be improved?
Competitors and suppliers are another large force influencing business activity:

The more competitors in the market the less power individual businesses have and many business decisions will be impacted:
- Price;
- Quality and product differentiation;
- Level of service offered.
Businesses in oligopolistic industries should also watch for new-entrants: the lower the barrier for new entrants, the more they should watch for potential new competition.

- The more suppliers the better for buying businesses. More suppliers mean higher bargaining power (prices, credit terms) due to the competition between them.
- When only few suppliers are available, the power lies with the sellers and not the buyers.
Businesses should also keep an eye on International Influences on their activities. Globalization has been leveraging such influence in recent years. Although International Trade makes it easier for businesses to buy and sell from/to other countries (increasing economic activity), it also brings countries a handful of problems:

- Loss of output and jobs from firms unable to compete;
- Higher dependence on imports of essential goods which can be dangerous;
- New businesses are less likely to succeed due to increased competition;
- Predatory pricing from foreign firms to eliminate competition may happen;
- Decrease in the local currency exchange rate due to an imbalance on imports vs. exports.

- International Trade Agreements have been strengthening International Trade by reducing tariffs and quotas (trade barriers) and improving imports & exports.
- In recent years there has been a push towards Free International Trade with the main purpose of decreasing protectionism.
- The WTO and the increasing number of Free-Trade Blocs are the main forces towards Free Trade.
---
Although there are problems with International Trade, its benefits are undoubtful:

- Wider choice for customers - better quality and lower price (competition);
- Access to raw materials by business which may not be available locally - improves business activity (industrialization);
- Specialization by countries in producing what they do most effectively (comparative advantage);
- Specialization leads to economies of scale (further increase in quality and decrease in prices);
- Living standards in countries engaging in trade should increase as a consequence of higher economic activity;
The use of technology has drastically improved communications and facilitated International Trade:

- Blockchain has improved security on transactions over the internet;
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: used to establish the most cost-effective shipping routes, manage traffic at ports, and translate e-commerce search queries from one language into other languages;
- Mobile Payments boosting ecommerce;
- Platforms combining products are services leveraging consumption.
--
All of these changes are to say that Multinational Businesses have become more common in today's world and their relationships with governments aren't to be ignored:
- They generate many jobs and so can influence economies;
- They may lobby politicians make favorable changes to them.
Being a multinational business brings many advantages to businesses:
Avoids protectionist barriers (tariffs/quotas) by having operations in the local country;
Brings them closer to their target market;
Creates opportunities for economies of scale;
Opens up access to some natural resources they would not have otherwise.
Becoming a multinational business is no easy job though:
There may be diseconomies of scale due to poor communication and coordination among the many branches and headquarters;
Finding capable HR in some countries can be a challenge and require heavy investments on trainings;
Pressure Groups can be a problem to deal with;
MNCs, therefore, bring a variety of impacts to host countries - both positive and negative:
- Exchange rate appreciation (due to initial investment and exports);
- Employment opportunities;
- Knowledge sharing;
- Growth of local businesses (suppliers);
- Tax revenues;
- Increase in GDP;
But... There can always be bad too:
- Exploitation of local workforce;
- Increased pollution;
- Small local business are unable to compete;
- Reduction in cultural identity;
- Profit repatriation;
- Depletion of natural resources.
Finally, there are also environmental influences on business activities to be considered. There is a growing trend for businesses to move towards more environmental friendly practices:
Reducing pollution;
Using low-energy equipment;
Using recycled materials;
Disposing of waste responsibly.
Businesses willing to adopt an environmental friendly strategy can have various benefits:
- Marketing and promotion advantages since customers are increasingly aware of environmental issues;
- Lower chances of court fines and pressure groups actions;
- Higher number of quality employment applications as businesses gain reputation;
- Long-term financial benefits can also be harvested from environmental investments - e.g. a large investment in solar energy today can pay off in the long-term as oil prices increase.
The switch to an environmental-friendly strategy does not come without its risks, though. Mostly because it's costly:
Competitors might be able to offer lower prices if no environmental efforts are made and customers might overlook the issue;
Investments in environmental-friendly processes can be expensive limiting the firm's ability to make higher profits;
Lower profits reduce further investments on other profit-making activities;
The investment might not be worth it as some countries do not apply fines and penalties to companies that adopt environmentally-harmful practices.
It's important that a company's environmental claims' are genuine...

Greenwashing: giving a false impression or providing misleading information about how a company’s products are environmentally sound and sustainable.
Businesses are voluntarily implementing Environmental Audits so that stakeholders can check and compare their achievements with other businesses in the field.
Managers are the ones setting the targets, reporting them, and working towards them;
Consumers use such audits as a guide to purchasing behavior;
Investors, particularly ethical ones (banks), will use such information for their decision-making;
Employees may be motivated by such initiatives and more/better applicants can be attracted.

Such audits are expensive and time-consuming to produce. Because they are not mandatory and do not have a unified standard they are also not viewed as credible by many.
Pressure group activity, government environmental laws and green consumerism are forcing most businesses to take more sustainable business decisions.
To-Do List
Term 1, Chapter 6 - Decision-Making Question #3 (p. 94, p.95)
Chapter 6 - External Influences on Business Activity












Comments